 |
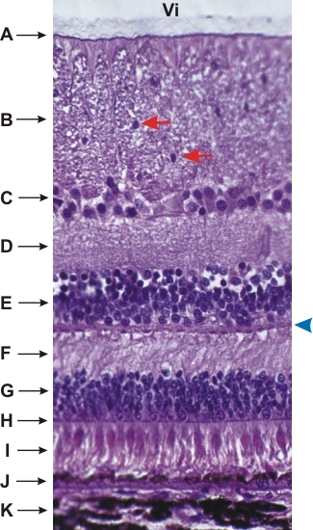
Retina of a dog’s eye.
The following structures or layers, from the vitreous body (Vi) down to the choroid (K), are identified:
- Basement membrane at the surface of the retina
- Layer of optic nerve fibres seen here in cross section (compare with Figure 18.28). Note the presence of the nuclei of neuroglia (red arrows).
- Ganglion cell layer
- Inner plexiform layer
- Inner nuclear layer
- Outer plexiform layer. The acidophilic plaques ( blue arrowhead) at the borderline between this layer and the inner nuclear layer are areas of synaptic connections.
- Outer nuclear layer
- Thin acidophilic layer corresponding to the zones of adhesions between processes of Müller’s fibres and rods and cones (see Figure 18.25)
- Layer of cones, with their large acidophilic ellipsoidal extremities, and layers of filiform rods
- Layer of pigmented epithelial cells. These protective cells eliminate by phagocytosis the desquamating extremities of the rods and cones.
- Choroid with melanocytes
Stain: H–E
Magnification: ×350
|


![]() The text and images of this Histology Atlas, by Yves Clermont,
Michael Lalli & Zsuzsanna Bencsath-Makkai,
are licensed under a
Creative Commons Attribution-Noncommercial-No Derivative Works 2.5 Canada Licence
and cannot be modified without the written permission of the authors.
Use of any text or images must carry an acknowledgement which includes a link to the original work.
The text and images of this Histology Atlas, by Yves Clermont,
Michael Lalli & Zsuzsanna Bencsath-Makkai,
are licensed under a
Creative Commons Attribution-Noncommercial-No Derivative Works 2.5 Canada Licence
and cannot be modified without the written permission of the authors.
Use of any text or images must carry an acknowledgement which includes a link to the original work.