|
||
| 11. Oral Cavity | ||
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 | ||
| 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 |
| |||
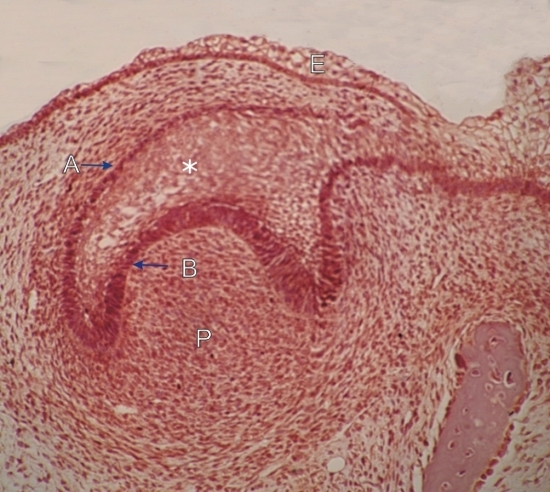 |
Section of the oral cavity of a pig embryo.
This field shows a very early stage of tooth formation. The primitive epithelium, or ectoderm, (E) lining the inside of the lip of the embryo grows in the underlying connective tissue, or mesoderm, to form a cupula or caplike epithelial structure. Inside this cupula is an accumulation of mesoderm that forms a primitive dental papilla (P). This papilla is the precursor of dental pulp. The cupula shows an outer dental epithelium (A) and an inner dental epithelium (B). These two epithelial cell layers of the cupula plus the epithelial cells between (*) form the enamel organ which contibutes to the formation of the enamel of the crown of the tooth (see following figures). Some mesodermal cells of the dental papilla differentiate into odontoblasts which produce the dentin of the crown. Later steps of the tooth formation are presented in the following figures. Stain: H–E
|
||