|
||
| 3. Muscle Tissue | ||
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 |
| |||
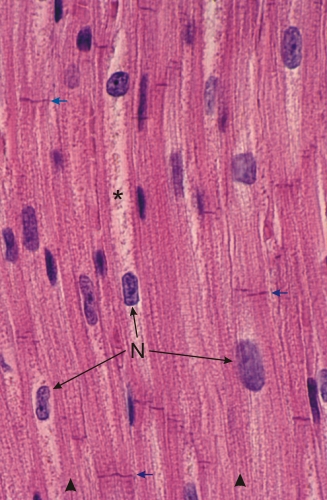 |
Section of cardiac muscle showing striated muscle fibres, or cardiocytes, cut longitudinally.
The individual myofibrils are visible (arrowheads below) but are less evident than those of the myofibrils of the skeletal muscle fibres. The demarcation of individual cardiocytes is unclear, but the extremities of the fibres are visible as chromophilic cross striations called intercalated discs (arrows). Such discs are sites of attachment of cardiocytes to each other (see Figure 3.1B). One or two nuclei (N) per cardiocyte occupy the centre of the fibres. These nuclei are surrounded by an abundant granulated cytoplasm (*). Most of these cytoplasmic granules correspond to mitochondria. In atrial cardiocytes, the cytoplasm also contains secretory granules containing the vasoactive substance called atrial natriuretic factor (ANF). Such secretory granules are not identifiable in the present section. Stain: H–E
|
||